Industrial automation and its advantages in warehousing
Industrial automation is becoming more widespread among companies nowadays. One of its greatest benefits is increased competitiveness.
What is industrial automation?
Industrial automation is the use of control systems such as robots, computers, and smart warehouses to manage manufacturing processes, machinery, and product distribution. Its primary goal is to improve productivity, quality, and material handling, often requiring companies to transition from manual techniques to more advanced solutions.
Automation and control systems encompass a wide range of machines, sensors, processors, and networks that connect industrial environments. Examples include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCSs), and supervisory control and data acquisition systems (SCADAs). Also falling under this category are cutting-edge technologies such as Industry 4.0 innovations, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Beyond enhancing productivity, these technologies free employees from repetitive tasks, enabling them to focus on processes where their expertise adds the most value.
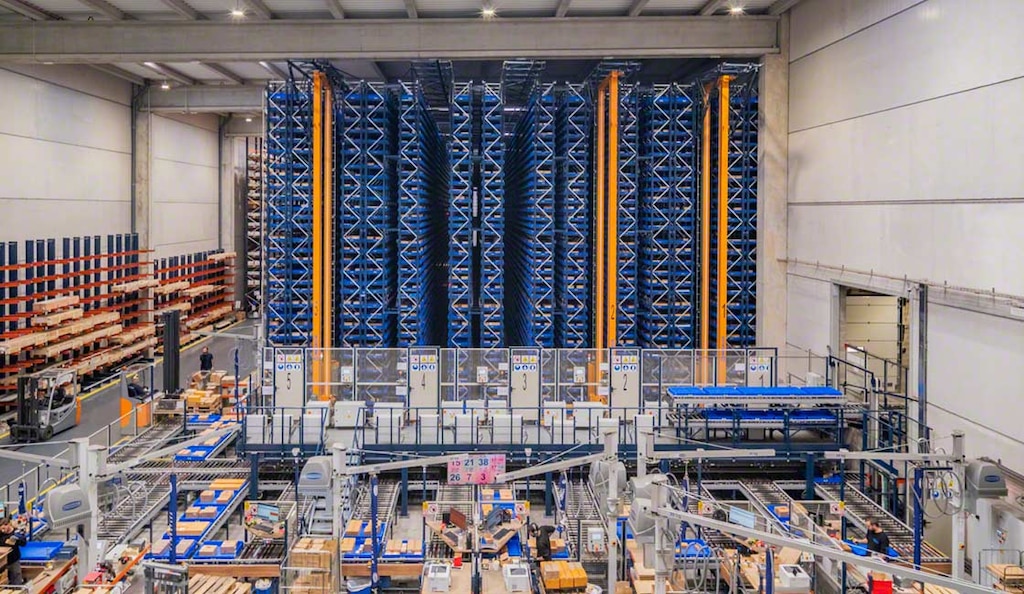

Features of industrial automation
Getting expert advice and venturing into the world of industrial automation brings companies numerous benefits:
- Increased productivity. Implementing an industrial automation project makes organizations more competitive by reducing damage caused by material handling or human errors in processes like order picking. This is one reason why more and more companies are investing in warehouse automation.
- Greater efficiency. Completing repetitive tasks quickly enables effective production line replenishment and swifter fulfillment of customer requests. It also allows workers to focus on more value-added tasks.
- Return on investment. The increase in speed leads to revenue generation typically exceeding the initial investment.
- Quality control. Reducing errors in production and distribution centers (DCs) improves product quality, which translates to greater customer satisfaction.
- Data collection. Automated systems are invaluable for gathering real-time, accurate information about available inventory and completed processes. This helps facilitate decision-making and anticipating situations.
- Safety. Delegating certain tasks to machines instead of humans bolsters occupational safety and health. Examples include removing products from high shelves or handling explosives in industries like mining or civil engineering.
- Sustainability. Industrial automation processes can lead to savings in heating, air conditioning, and lighting. In fact, lights-out warehouses already exist, where operations run without human presence.
Examples of industrial automation
Technological advancements have reached various sectors, each of which uses automated tools for specific tasks. In the automotive industry, applications include component assembly and the welding of car bodies. In sectors like food and cosmetics, industrial automation involves tasks such as product packaging, labeling, and placing into boxes for subsequent distribution.
Similarly, automated systems are valuable for inspection tasks and monitoring/controlling storage conditions, which is crucial when working with temperature-sensitive items.

Numerous production companies have automated their warehouses to streamline operations and improve responsiveness to market needs:
- Schaal Chocolatier. The high-end chocolate manufacturer wanted to move away from traditional operator-driven forklifts. It ran a warehouse automation project in Geispolsheim (France), installing Mecalux stacker cranes for pallets and a conveyor system. This setup maintains the low temperatures required to preserve its chocolate and thus the quality.
- JC Valves. This Spanish multinational, which manufactures and markets high-quality valves for industries worldwide, automated all operations in its Sant Boi de Llobregat center. Goods are received and shipped autonomously, without manual handling. Its two automated storage and retrieval systems are connected to production to supply raw materials and receive finished products.
- Konya Şeker. The Turkish producer of sugar, sweets, and other derivatives opened an automated rack-supported building at its Çumra plant, which features 27 production lines and an annual output of over 480,000 tons. The autonomous exchange of raw materials and finished goods enables the company to distribute 2,000 pallets daily.
Types of industrial automation
There are several kinds and levels of industrial automation. These are the most common:
- Fixed automation. Fixed (or hard) automation typically doesn’t allow for modifications, as they would be costly. It’s suitable for specific repetitive tasks such as packaging.
- Flexible automation. Also known as soft automation, this allows for changes in product design or the organization of goods within a DC.
- Integrated automation. These systems completely eliminate the need for human intervention and can operate autonomously.
- Programmable automation. Often associated with production runs, this variety allows for reprogramming machinery software to carry out different operations to accommodate products.
Kickstart your warehouse automation with Interlake Mecalux
Are you looking to streamline your operations using the latest technologies and expert guidance? Interlake Mecalux is here to help. With over 55 years of experience in manufacturing and implementing intralogistics solutions, we continuously innovate and refine our products to optimize our clients’ capabilities. Contact us without obligation. We’ll show you which storage and software solutions have the greatest potential to take your logistics operations to the next level.
