
Waybill for goods transportation
A waybill is a key document in international trade. It serves as a transportation contract to ensure regulatory compliance and cargo security.
What is a waybill?
A waybill is a legal document that contains information about goods being shipped. It functions as a contract for product transfers, detailing the items being distributed, the carriers, the recipients, and the terms and conditions of transportation. Another name for a waybill is a bill of lading, a term traditionally used for maritime transportation. However, outside the US, a bill of lading can serve as a document of title, transferring ownership of the cargo.
The waybill accompanies the goods from shipment to delivery to customers. It can include these details:
- Place and date of issuance.
- Expected delivery location.
- Name and address of the sender (consignor), recipient (consignee), and carrier.
- Nature of the goods and packaging.
- Number of packages.
- Weight of the goods.
- Instructions for customs.
- Transportation-related costs.
- Notes on cash-on-delivery payments, if applicable.
Example of a waybill
Below is a sample waybill that could serve as a template. As it’s a generic model, the fields may vary depending on the type of shipment.
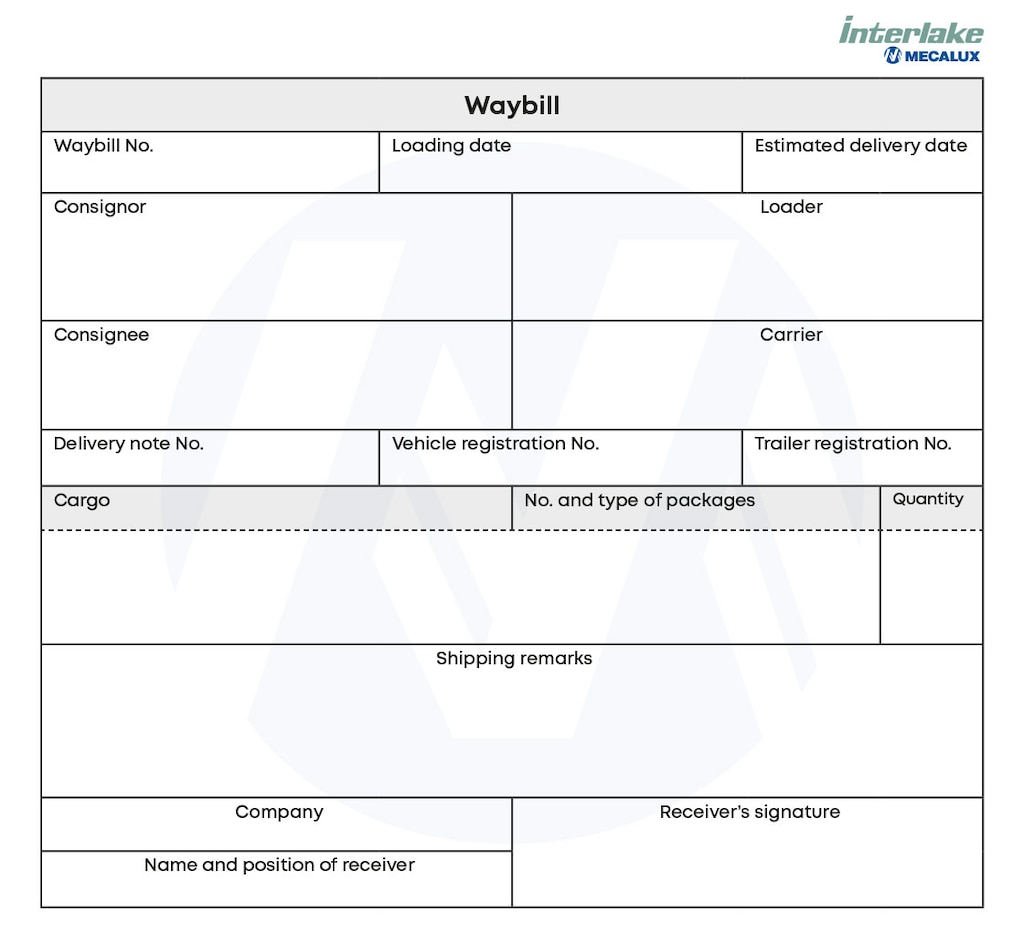
This legal document typically includes three copies: one for the consignor, another for the carrier, and a third that accompanies the goods along their journey.
Digital waybill
In recent years, digital waybills have become popular. This electronic format streamlines information exchange between the consignor, carrier, and consignee while providing a detailed online record of the entire transportation process.
Once the goods are dispatched, both the company and the delivery agency can consult the shipping waybill digitally, eliminating the need for printed copies. It can be digitally signed, enabling immediate data access and allowing clients to track and monitor their shipments in real time.
Who issues the waybill?
The party charged with sending the waybill or bill of lading is usually the consignor of the goods. This would be the company or person shipping the products through a carrier.
However, who’s responsible for drafting the waybill? This isn’t always so clear. In some cases, the carrier may also issue the document, particularly when providing a specific service or acting as a maritime shipping agent.
Regardless of which party issues it, the waybill must contain all required details to guarantee the safe, efficient carriage of the goods. This includes the description, quantity, weight, declared value, and transportation conditions.
When is a waybill not necessary?
A waybill is not mandatory in certain situations, such as:
- Private transportation of goods using company-owned vehicles.
- Shipment of personal belongings, as in the case of moving to a new home.
- Parcel delivery services within the same city or region, where no borders are crossed.
- Carriage of low-value goods, depending on the regulations of the country and transportation mode.
It’s advisable to check the applicable requirements for each case.
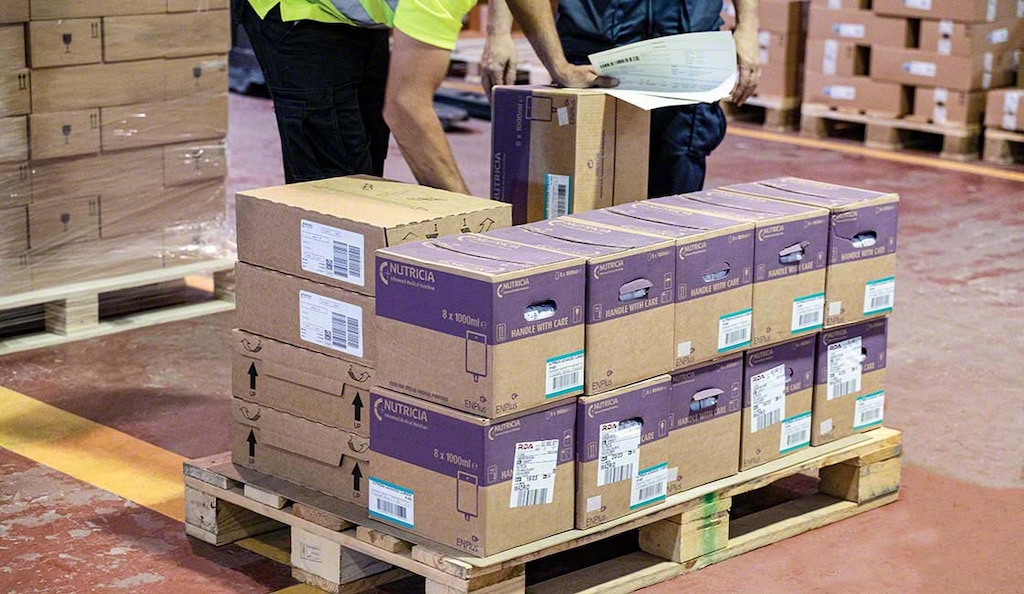

What is the purpose of a waybill? How is it used in warehousing?
Waybills are essential for freight delivery, serving several functions in logistics management.
- Formal contract. This document represents a formal agreement between the sender and the carrier. It specifies the service conditions for national transport (domestic waybill) and international transport (international waybill). This contract regulates the commercial relationship, ensuring both parties understand their obligations.
- Official receipt. The waybill confirms that the cargo has been delivered under the agreed conditions. By signing it, the carrier assumes responsibility for the goods. This documentation serves as a reference in case of disputes or claims.
- Evidence of ownership. In the form of a bill of lading, the document can demonstrate title to the goods during transit. This is especially critical in international trade operations or for merchandise whose ownership changes during transportation.
- Tracking and traceability. The waybill or bill of lading enables shipment traceability and monitoring along the supply chain, providing detailed information about the origin, destination, quantity, and condition of the cargo.
In a warehouse, the waybill is used during goods receipt to verify the quantity, condition, and description of the items arriving at the facility. By maintaining stricter control over incoming and outgoing products, companies can improve inventory management.
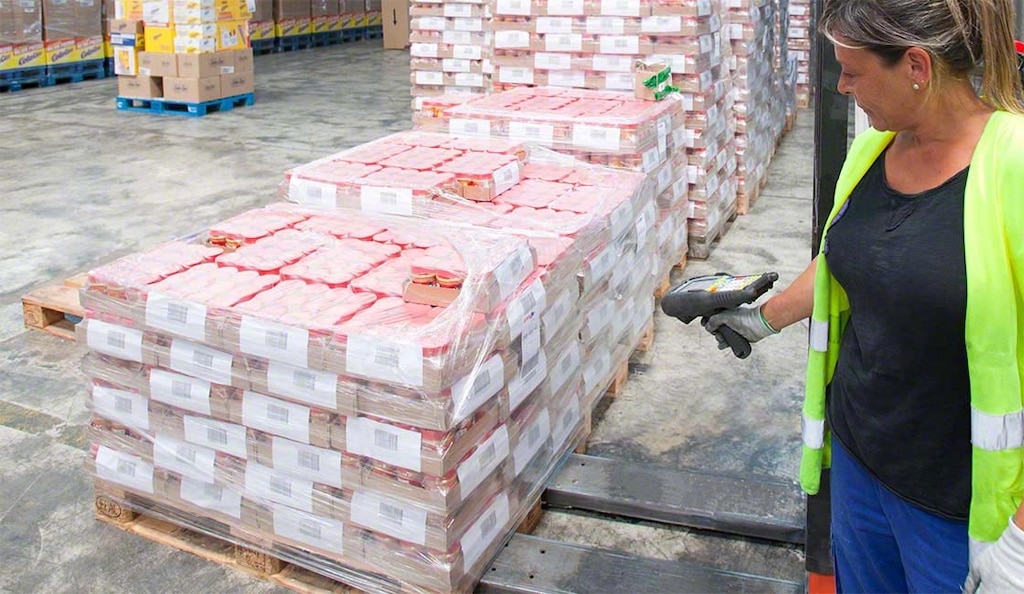

Digitalization: Key for freight shipment
Digitalization is crucial for guaranteeing efficiency and compliance in goods transportation. Waybills can benefit from tools like a warehouse management system (WMS). In addition to optimizing logistics operations, this software reduces errors in product distribution. Solutions like Interlake Mecalux’s Easy WMS stand out for their ability to streamline inventory management.
The WMS sends instructions to staff to ensure that each order contains all items requested by customers. Moreover, it automatically records the necessary details to complete the waybill, such as the goods’ description, quantity, weight, and transportation conditions. The WMS software also generates shipment reports, providing a printed summary of each outgoing order. This not only saves time but also limits errors, contributing to more agile and secure shipment management.
Do you have questions about how to optimize the management of your shipments? Or perhaps you’re looking to implement digital solutions like a WMS to improve your logistics operations. Either way, our expert team is here to help. Contact us to learn more about how our solutions can transform your warehouse operations.
