
Cycle stock and what it means for inventory management
Cycle stock (or working inventory) refers to the level of inventory available to meet typical demand. Analyzing historical data and demand forecasts provides more detailed knowledge of your exact cycle stock levels.
By calculating cycle stock, companies ensure they have all the goods they need to prepare orders every day and satisfy customer demand.
What is cycle stock?
Cycle stock is the part of a business’s inventory intended to fulfill sales orders in a given period. This stock control method lets companies know the optimal stock levels their warehouse or physical store should have to respond to normal product demand.
Cycle stock plays a key role in an organization’s accounting system, as it’s used to meet standard demand for a product. Knowing exactly how much cycle stock you need is crucial for optimizing inventory efficiency. If there’s a sudden increase in product demand ― or an inaccurate forecast ― the company will be forced to resort to its reserve stock to avoid a stockout. On the other hand, too many units of a SKU could limit cash flow and push up warehousing logistics costs.
To calculate your ideal inventory levels, it’s essential to analyze demand regularly. Organizations can improve their inventory management by implementing software solutions that analyze historic demand levels and take into account logistics information such as seasonality, stock turnover, and product life cycles.
Cycle stock is used in all kinds of facilities. In the warehouse, it constitutes a metric for inventory management, and in production centers, it’s applied to calculate product demand to keep up with manufacturing orders.
What is the difference between cycle stock and safety stock?
While cycle stock relates to the amount of product a company uses to satisfy its regular orders, safety stock refers to the reserve inventory employed for unexpected peaks in product demand.
The main function of safety stock is to protect a business’s logistics operations from unforeseen changes in buying trends, insufficient coordination on the production lines, and even supply chain disruptions.
In other words, safety stock serves to cover possible spikes in product demand over a specific period. For example, if a business receives an unusually large quantity of requests for a SKU, operators will first fill orders with cycle stock. When that’s been exhausted, they’ll make use of safety stock. At the same time, the manager will recalculate the optimal inventory level for the new demand and place the corresponding order with the supplier.

Benefits of forecasting cycle stock
Analyzing and predicting the stock quantities you need to fill average orders is a key factor in inventory management. These are the main advantages of calculating your cycle stock regularly:
- Efficient logistics service: consistent control of cycle stock levels means that companies always have enough product to satisfy customer demand. Fulfilling orders fosters customer satisfaction. And as a result, it increases the likelihood of business growth.
- Optimized warehousing costs: calculating cycle stock routinely will limit overstock in your facility. Excess warehouse inventory raises storage and electricity costs and complicates goods handling.
- Control of safety stock: logistics planning that includes inventory management avoids the needs to draw on safety stock. This merchandise should be reserved for one-off scenarios, e.g., a supply chain disruption or a significant and unexpected increase in demand for a particular SKU.
How do you calculate cycle stock?
One of the most common ways to calculate cycle stock is using the economic order quantity (EOQ) formula, also known as the Wilson formula. This determines when you should place an order with a supplier and in what quantity to ensure inventory availability. The EOQ formula is calculated by means of the following variables:
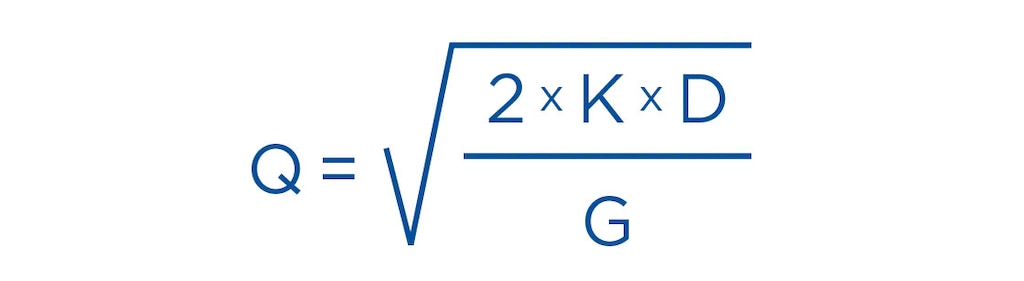
Q = optimal order quantity
K = cost of placing each order
D = annual demand quantity
G = storage cost
The EOQ formula ensures that your company will have enough stock to satisfy your normal customer demand. By incorporating the storage cost variable, the EOQ takes into consideration logistics costs to obtain the optimal stock levels your warehouse needs for each product.

Cycle stock: inventory you need to fill warehouse orders
Calculating your cycle stock regularly will ensure efficient inventory control in your facility. Nevertheless, computing cycle stock by means of mathematic formulas entails the risk of human error.
There are tools that partially automate the calculation of stock management formulas (e.g., Microsoft Excel). However, to minimize the risk of error in inventory control, you have to implement WMS software. These programs ensure product traceability and coordinate all logistics processes taking place in the facility.
This is the case of Interlake Mecalux’s modern Easy WMS software, which provides real time stock control and seamlessly organizes companies’ logistics operations. Interested in boosting productivity and efficiency in your warehouse? Don’t hesitate to contact us. One of our expert consultants will advise you on the best solution for your business.
